Press release
Analysis Showcases Potential for More Complete Revascularizations with Impella Compared to IABP during HRPCI
DANVERS, Mass., May 18, 2023 – Abiomed, part of Johnson & Johnson MedTech[1], announces results of a third-party analysis showing that utilizing Impella during high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) procedures may help physicians achieve a more complete revascularization compared to high-risk PCIs supported using an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP). Previous studies have shown that a more complete revascularization can lead to longer survival[2],[3], a greater reduction in heart failure and angina symptoms[4], and an improved quality of life for the patient[5].
This analysis shows more patients achieved a more complete revascularization with Impella than with IABP support during high-risk PCIs (see Figure 1; p for categorical allocation <0.001). Vasileios Panoulas[6], MD, FRCP, PhD, FESC, consultant interventional cardiologist, Royal Brompton and Harefield hospitals, presented this data during EuroPCR 2023, the annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI), which took place in Paris, France, from May 16-19, 2023.
The PROTECT II Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT), PROTECT III and RESTORE-EF prospective studies were included in this analysis and individual patient data were pooled between these three studies. Coronary artery disease severity was measured pre-PCI using SYNTAX score[7] and post-PCI using residual SYNTAX Score (rSS)[8]. The analysis compared complete revascularization rates, as measured by rSS<2, between high-risk PCI patients who received Impella support (N=880) and IABP support (N=155).
Results of a multiple regression analysis showed a 40% greater reduction of residual SYNTAX Score post-PCI in patients treated with Impella compared to IABP (95% CI 27-50%, p<0.001). Defining complete revascularization (CR) as rSS<2, CR was achieved in 42.2% of Impella patients vs. 20.6% of IABP patients. “When taking study limitations into account, this pooled analysis showcases the potential of Impella to contribute to improved long-term patient outcomes by allowing a greater extent and quality of revascularization,” said Panoulas.
Previous studies have shown that a more complete revascularization is associated with longer patient survival and patients with residual SYNTAX Score >8 were associated with 37% all-cause mortality at five years against 9% for rSS=0 (HR=5.12, 95% CI 3.32-7.90, P<0.001)[9]. In other meta-analyses, rSS=0 was associated with 29% lower all-cause mortality (p=0.001) and 25% fewer major adverse events (p<0.001)[10].
This analysis supports the hypotheses incorporated in the ongoing PROTECT IV RCT. PROTECT IV is an on-label, prospective, multi-center RCT designed to provide the level of clinical evidence needed to achieve a global Class I guideline recommendation for Impella in high-risk PCI in the future.
The pooled data analysis was led by the York Health Economics Consortium (YHEC), an independent research company owned by the University of York (England).
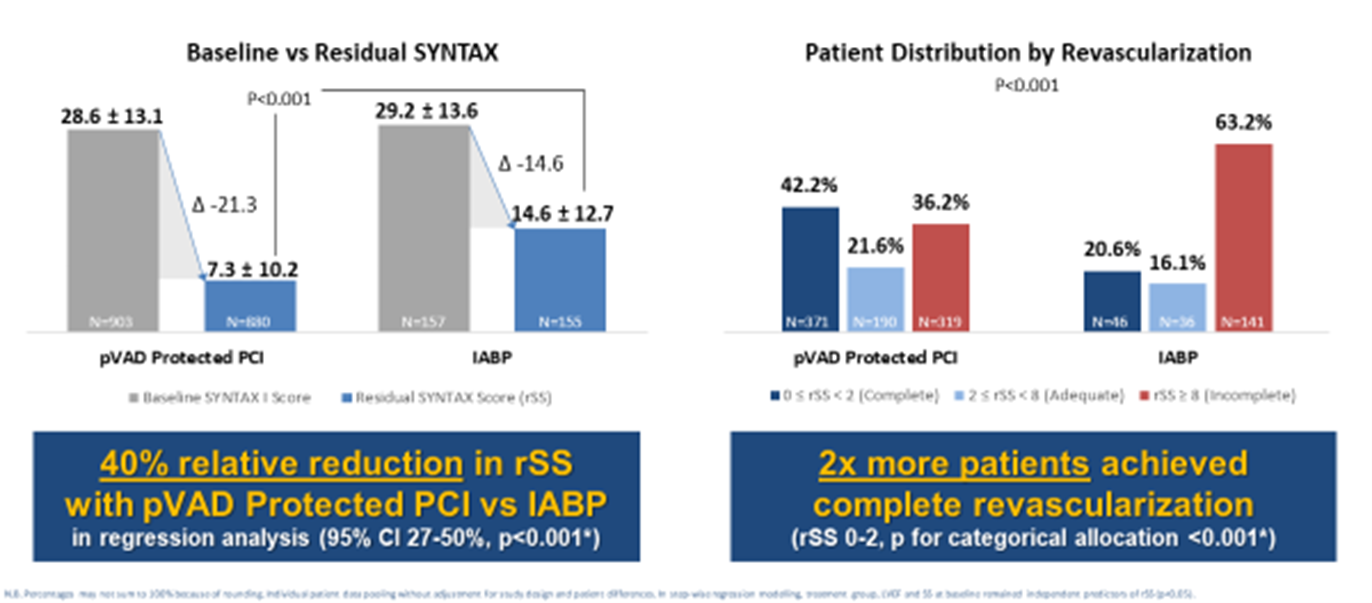
Figure 1. Results from the PROTECT II RCT, PROTECT III and RESTORE-EF Pooled Data Analysis
*An earlier version of this statement erroneously stated Dr. Panoulas received honoraria from Abiomed, Inc.
About Abiomed
Based in Danvers, Massachusetts, USA, Abiomed, part of Johnson & Johnson MedTech, is a leading provider of medical technology that provides circulatory support and oxygenation. Our products are designed to enable the heart to rest and recover by improving blood flow and/or provide sufficient oxygenation to those in respiratory failure. For additional information, please visit www.abiomed.com.
About Johnson & Johnson MedTech
At Johnson & Johnson MedTech, we unleash diverse healthcare expertise, purposeful technology, and a passion for people to transform the future of medical intervention and empower everyone to live their best life possible. For more than a century, we have driven breakthrough scientific innovation to address unmet needs and reimagine health. In surgery, orthopaedics, vision, and interventional solutions, we continue to help save lives and create a future where healthcare solutions are smarter, less invasive, and more personalized.
Cautions Concerning Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains “forward-looking statements” as defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 regarding Impella 2.5, Impella CP and Impella CP with SmartAssist. The reader is cautioned not to rely on these forward-looking statements. These statements are based on current expectations of future events. If underlying assumptions prove inaccurate or known or unknown risks or uncertainties materialize, actual results could vary materially from the expectations and projections of Abiomed, Inc., any of the other Johnson & Johnson MedTech Companies and/or Johnson & Johnson. Risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to: uncertainty of commercial success; challenges to patents; competition, including technological advances, new products and patents attained by competitors; manufacturing difficulties and delays; product efficacy or safety concerns resulting in product recalls or regulatory action; changes to applicable laws and regulations, including global health care reforms; changes in behavior and spending patterns of purchasers of health care products and services; and trends toward health care cost containment. A further list and descriptions of these risks, uncertainties and other factors can be found in Johnson & Johnson’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 1, 2023, including in the sections captioned “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and “Item 1A. Risk Factors,” and in Johnson & Johnson’s subsequent Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q and other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Copies of these filings are available online at www.sec.gov, www.jnj.com or on request from Johnson & Johnson. None of Abiomed, Inc., the Johnson & Johnson MedTech Companies nor Johnson & Johnson undertakes to update any forward-looking statement as a result of new information or future events or developments.
For further information please contact:
Jenny Leary
Associate Director, US Communications
[email protected]
978-882-8491
References
-
Abiomed, Inc. is part of Johnson & Johnson MedTech, which comprises the surgery, orthopedics, vision and interventional solutions businesses within Johnson & Johnson's MedTech segment.
-
Garcia S, Sandoval Y, Roukoz H, et al. Outcomes after complete versus incomplete revascularization of patients with multivessel coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis of 89,883 patients enrolled in randomized clinical trials and observational studies. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;62:1421-31.
-
Nagaraja V, Ooi SY, Nolan J, et al. Impact of Incomplete Percutaneous Revascularization in Patients With Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Am Heart Assoc 2016;5.
-
National Institute of Health and Care Excellence. Stable Angina: Management. Clinical Guideline [CG126]. NICE, 2011. Available from https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg126/chapter/Guidance#investigation-and-revascularisation. Accessed on May 12, 2023.
-
Mehta SR, Wang J, Wood DA, et al. Complete Revascularization vs Culprit Lesion-Only Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Angina-Related Quality of Life in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Results From the COMPLETE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol 2022;7:1091-1099.
-
Dr. Panoulas has received consulting fees and honoraria from Abiomed Europe GmbH.
-
Sianos G, Morel MA, Kappetein AP, et al. The SYNTAX Score: an angiographic tool grading the complexity of coronary artery disease. EuroIntervention 2005;1:219-27.
-
Genereux P, Palmerini T, Caixeta A, et al. Quantification and impact of untreated coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention: the residual SYNTAX (Synergy Between PCI with Taxus and Cardiac Surgery) score. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;59:2165-74.
-
Farooq V et al. Quantification of incomplete revascularization and its association with 5-year mortality in the SYNTAX trial validation of the residual SYNTAX score. Circulation 2013;128:141-51.
-
Ahn JM et al. Comparison of Stenting Versus Bypass Surgery According to the Completeness of Revascularization in Severe Coronary Artery Disease: Patient-Level Pooled Analysis of the SYNTAX, PRECOMBAT, and BEST Trials. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2017;10:1415-1424.